1.什么是云计算
云计算(cloud computing,台湾译作云端运算),是分布式计算技术的一种,其最基本的概念,是透过网络将庞大的计算处理程序自动分拆成无数个较小的子程序,再交由多部服务器所组成的庞大系统经搜寻、计算分析之后将处理结果回传给用户。透过这项技术,网络服务提供者可以在数秒之内,达成处理数以千万计甚至亿计的信息,达到和“超级计算机”同样强大效能的网络服务。
云计算是一种资源交付和使用模式,指通过网络获得应用所需的资源(硬件、平台、软件)。提供资源的网络被称为“云”。“云”中的资源在使用者看来是可以无限扩展的,并且可以随时获取。这种特性经常被比喻为像水电一样使用硬件资源,按需购买和使用。[1](Cloud computing is a resource delivery and usage model, it means get resource (Hardware, software)via network. The network of providing resource is called ‘Cloud’. The hardware resource in the ‘Cloud’ seems scalable infinitely and can be used whenever.)[2]
最简单的云计算技术在网络服务中已经随处可见,例如搜寻引擎、网络信箱等,使用者只要输入简单指令即能得到大量信息。
未来如手机、GPS等行动装置都可以透过云计算技术,发展出更多的应用服务。
进一步的云计算不仅只做资料搜寻、分析的功能,更可计算一些像是分析DNA结构、基因图谱定序、解析癌症细胞等。
稍早之前的大规模分布式计算技术即为“云计算”的概念起源[1]。
Google目前的云技术,主要由MapReduce、GFS及BigTable三项所组成
2.云在计算机中的含义
云是指因特网,因过去一直将因特网画成一朵云。
3.云计算的组件
云端储存(cloud storage)是一种将数据保存在虚拟服务器上的数据类型,通常意义上,数据存储在第三方媒介,而非特定单一服务器上。
4.云计算的推广与发展
2007年10月,Google与IBM开始在美国大学校园,包括卡内基美隆大学、麻省理工学院、史丹佛大学、加州大学柏克莱分校及马里兰大学等,推广云计算的计划,这项计划希望能降低分布式计算技术在学术研究方面的成本,并为这些大学提供相关的软硬件设备及技术支援(包括数百台个人计算机及BladeCenter与System x服务器,这些计算平台将提供1600个处理器,支援包括Linux、Xen、Hadoop等开放源代码平台)。而学生则可以透过网络开发各项以大规模计算为基础的研究计划[1]。
2008年1月30日,Google宣布在台湾启动“云计算学术计划”,将与台湾大学、台湾交通大学等学校合作,将这种先进的大规模、快速计算技术推广到校园[3]。
2008年8月3日,美国专利商标局(以下简称“SPTO”)网站信息显示,戴尔正在申请“云计算”(Cloud Computing)商标,此举旨在加强对这一未来可能重塑技术架构的术语的控制权。戴尔在申请文件中称,云计算是“在数据中心和巨型规模的计算环境中,为他人提供计算机硬件定制制造”。[4]。
5.云计算与IT技术[1]
云计算是随着处理器技术、虚拟化技术、分布式存储技术、宽带互联网技术和自动化管理技术的发展而产生的. 这种大规模的计算能力通常是由分布式的大规模集群和服务器虚拟化软件搭建。(Cloud computing and technology:New advances in processors, virtualization technology, distributed storage, broadband Internet access , automated management and fast, inexpensive servers have all combined to make cloud computing a compelling paradigm.This vast process power is usually got with a distributed, large-scale server cluster and server virtualization software.)
6.云计算使用模式[1]
传统的计算模式下,单台台式机的资源用来完成任务。在客户服务器模式下,服务器用来执行任务。在云计算模式下,网络超级计算机—“云”用来执行任务。用户能在任何时间任何地点通过互联网获取计算、存储、网络资源,并且能够按照处理器利用率、存储使用量、带宽消耗付费。(Cloud computing usage model:In traditional computing model, tasks are completed using a single desktop computer. In the client/serer model, tasks are completed using a remote server. In cloud computing model, tasks are completed using ‘Cloud’-a network super computer.Cloud computing allows users and companies to pay for and use the services and storage that they need, when they need them and, as wireless broadband connection options grow, where they need them. Customers can be billed based upon server utlilization, processing power used or bandwidth consumed.)
7.云计算的影响[1]
云计算有可能颠覆软件产业,应用和许可被随时购买和生效,应用在网络上而不是本机上运行。这种转变将数据中心放在网络的核心位置,而所有的应用所需要的计算能力、存储、带宽、电力都由数据中心提供。云计算不仅影响商业模式,还影响开发、部署、运行、交付应用的方式。(Cloud computing impact:As a result, cloud computing has the potential to upend the software industry entirely, as applications are purchased, licensed and run over the network instead of a user's desktop. This shift will put data centers and their administrators at the center of the distributed network, as processing power, electricity, bandwidth and storage are all managed remotely. It affects not only business models, but the underlying architecture of how we develop, deploy, run and deliver applications.)[5]
8.云计算对服务提供商意味着什么[1]
- 快速部署(Fast Provision)
- 缩小主机规模(Reduce servers scale)
- 提高资源利用率(Increase resource utilization rate)
- 提高管理效率(Improve management efficiency)
- 降低运维成本(Lower maintenance cost)
- 基础设施可以放置在低土地和能源成本的地区(Location of infrastructure in areas with lower costs of real estate and electricity)
- 提供商业连续性服务(Provide business continuity service)
- 提高管理效率(Improve management efficiency)
- 提高服务水平(Improve service levels)
- 复杂的体系结构(Complex architecture)
- 商业模式和理念的转变(Change of business model and faith)
9.云计算对于用户意味着什么[1]
- 用户端负载降低(Lower client workload)
- 降低总体拥有成本(Lower Total Cost Ownership)
- 可能将应用的开发与基础设施维护相对分离(Separation of infrastructure maintenance duties from domain-specific application development)
- 可能将程序代码与物理资源分离(Separation of application code from physical resources)
- 不需要为一次性任务或罕见的负载状况准备大量设备(Not have to purchase assets for one-time or infrequent intensive computing tasks)
- 按需扩展资源(Expand resource on-demand)
- 使应用具有高可用性(Make the application have high availability)
- 快速部署应用(Quickly deploy application)
- 按使用付费(Pay per use)
10.云计算基础设施基本特征[1]
- 自愈合(Self-healing)
- 多用户使用(Multi-tenancy)
- 虚拟化(Virtualized)
- 线形扩展(Linearly ScalableLinearly Scalable)
- 资源监控和测量(Resource Monitor and measure)
- 资源注册和发现(Resource registration and discovery)
11.云计算的关联概念[1]
云计算正成为行业中的热点概念。它和下面的词汇产生了或多或少的关连:网格计算,效用计算,虚拟化,服务器集群,主机租用,主机托管。云计算平台普遍用到了虚拟化技术,并且基于一个集群来构建,和网格计算和效用计算以及SaaS有着天然的联系,而且被用在IDC行业与主机租用和主机托管业务竞争。(Cloud computing’s brother buzzwords:Cloud computing is becoming one of the next industry buzz words. And it has more or less relation with these words: grid computing, utility computing, virtualization, server cluster, Dedicated server, Colocation. Cloud computing infrastructure usually use virtualization technology, and is built based on a server cluster, have nature relation to grid computing and utility computing, and is use to compete with Dedicated server and Colocation.)
云计算异军突起
相对与云计算的兄弟概念而言,云计算只是刚刚兴起。从Google Trend 获取的信息我们可以看到,云计算在2007年末才被该系统统计,并且一直处于上升趋势。而同时,网格计算、效用计算、分布式计算的概念却呈现下降趋势。云计算和虚拟化应该会在托管平台上有所作为,而主机租用已经呈现下降趋势。(Cloud computing break out:Compared to its brother buzzwords, cloud computing is just beginning. Trends in usage of the terms from Google searches shows Cloud Computing is a relatively new term introduced in the past year. There has also been a decline in general interest of Grid, Utility and Distributed computing. Cloud Computing and Virtualization are the next hot hosting platforms; the Dedicated server term is slowly starting to lose ground vs. Virtualization and Cloud Computing.)
云计算和效用计算的比较
效用计算是一种提供计算资源的商业模式,用户从计算资源供应商获取和使用计算资源并基于实际使用的资源付费。简单说,是一种基于资源使用量的付费模式。效用计算主要给用户带来经济效益。企业数据中心的资源利用率普遍在20%左右,这主要是因为超额部署—购买比平均所需资源更多的硬件一边处理峰值负载,可预计到的或不可预计的。效用计算则允许用户只为他们所需要用到并且已经用到的那部分资源付费。(Utility computing is a business model of providing computing resource, user get and use the computing resource from service provider and pay for practically used resource. To say it simply, it is a price model based on resource usage quantity. The main benefit of utility computing is better economics. Corporate data centers are notoriously underutilized, with resources such as servers often idle 85 percent of the time. This is due to overprovisioning — buying more hardware than is needed on average in order to handle peaks (such as the opening of the Wall Street trading day or the holiday shopping season), to handle expected future loads and to prepare for unanticipated surges in demand. Utility computing allows companies to only pay for the computing resources they need, when they need them.)
效用计算是是一种分发应用所需资源的计费模式。 云计算是一种计算模式, 代表了在某种程度上共享资源进行设计、开发、部署、运行应用,以及资源的可扩展收缩和对应用连续性的支持。效用计算通常需要云计算基础设施支持,但并不是一定需要。同样,在云计算之上可以提供效用计算,也可以不采用效用计算。(Comparison of Utility Computing and Cloud Computing:Utility computing is a business model, it is a type of price model to deliver application infrastructure resource. Cloud computing is a computing model, relates to the way we design, build, deploy and run applications that operate in a sharing resources and boasting the ability to dynamically grow, shrink and self-heal. Utility computing is often need a cloud computing infrastructure, but not must need. Sameness, above the cloud computing, we can adopt utility computing, and, we can adopt other price model.)[6][7][8]
分布式计算
分布式计算是指在一个松散或严格约束条件下使用一个硬件和软件系统处理任务,这个系统包含多个处理器单元或存储单元,多个并发的过程,多个程序。一个程序被分成多个部分,同时在通过网络连接起来的计算机上运行。分布式计算类似于并行计算,但并行计算通常用于指一个程序的多个部分同时运行于某台计算机上的多个处理器上。所以,分布式计算通常必须处理异构环境、多样化的网络连接、不可预知的网络或计算机错误。(Distributed Computing:Distributed computing deals with hardware and software systems containing more than one processing element or storage element, concurrent processes, or multiple programs, running under a loosely or tightly controlled regime.In distributed computing, a program is split up into parts that run simultaneously on multiple computers communicating over a network. Distributed computing is a form of parallel computing, but parallel computing is most commonly used to describe program parts running simultaneously on multiple processors in the same computer. Both types of processing require dividing a program into parts that can run simultaneously, but distributed programs often must deal with heterogeneous environments, network links of varying latencies, and unpredictable failures in the network or the computers.)[9][10]
云计算与网格计算的不同点
网格计算是指分布式计算中两类比较广泛使用的子类型。一类是,在分布式的计算资源支持下作为服务被提供的在线计算或存储。另一类是,一个松散连接的计算机网络构成的一个虚拟超级计算机,可以用来执行大规模任务。该技术通常被用来通过志愿者计算解决计算敏感型的科研、数学、学术问题,也被商业公司用来进行电子商务和网络服务所需的后台数据处理、经济预测、地震分析等。(Grid computing:Grid computing is a term for either of two broad subcategories of distributed computing: 1 Online computation or storage offered as a service supported by a pool of distributed computing resources, also known as utility computing, on-demand computing, or cloud computing. Data grids provide controlled sharing and management of large amounts of distributed data, often used in combination with computational grids. 2 The creation of a "virtual supercomputer" composed of a network of loosely-coupled computers, acting in concert to perform very large tasks. This technology has been applied to computationally-intensive scientific, mathematical, and academic problems through volunteer computing, and it is used in commercial enterprises for such diverse applications as drug discovery, economic forecasting, seismic analysis, and back-office data processing in support of e-commerce and web services.[11]
网格计算强调资源共享,任何人都可以做为请求者使用其它节点的资源,任何人都需要贡献一定资源给其他节点。网格计算强调将工作量转移到远程的可用计算资源上。云计算强调专有,任何人都可以获取自己的专有资源,并且这些资源是由少数团体提供的,使用者不需要贡献自己的资源。在云计算中,计算资源被转换形式去适应工作负载,它支持网格类型应用,也支持非网格环境,比如运行传统或Web2.0应用的三层网络架构。
网格计算侧重并行的计算集中性需求,并且难以自动扩展。云计算侧重事务性应用,大量的单独的请求,可以实现自动或半自动的扩展。(Grid computing emphasizes on resource sharing, every grid node can apply for resource from other nodes, and every node should contribute resource to the grid. The focus of grid computing is on the ability of moving a workload to the location of theneeded computing resources, which are mostly remote and are readily available for use.Grids also require applications to conform to the grid software interfaces.Cloud computing emphasize on proprietary, every user out of the cloud can get it’s own private resource from the cloud, and the cloud resource are provided by the specific service provider, the user need not contribute its resource. In a cloud environment, computing resouces, such as servers, can be dynamically shaped or carved out from its underlying hardware infrastructure and made available to a workload. In addition, while a cloud does support grid, a cloud can also support nongrid environments,such as a three-tier Web architecture running traditional or Web 2.0 applications.Grid computing emphasizes on computing sensitive task, and is difficult to automated scale. Cloud computing emphasizes on transactional application, a great amount of separate request, and can scale automatically or semiautomatically.)[12][13][14]
服务器集群
服务器集群是指将一组服务器关联起来,使它们在外界从很多方面看起来如同一台服务器。集群内的服务器之间通常通过局域网连接,通常用来改善性能和可用性,但一般而言比具有同等性能功能和可用性的单台主机具有更低的成本。(Computer cluster:A computer cluster is a group of coupled computers that work together closely so that in many respects they can be viewed as though they are a single computer. The components of a cluster are commonly, but not always, connected to each other through fast local area networks. Clusters are usually deployed to improve performance and/or availability over that provided by a single computer, while typically being much more cost-effective than single computers of comparable speed or availability.[15])
网格通常更加松散连接、异构、地理位置分散,主机之间信任度更低。(Grids tend to be more loosely coupled, heterogeneous, and geographically dispersed, grid computers do not fully trust each other.)
虚拟化
虚拟化指对计算资源进行抽象的一个广义概念。虚拟化对上层应用或用户隐藏了计算资源的底层属性。它既包括使单个的资源(比如一个服务器,一个操作系统,一个应用程序,一个存储设备)划分成多个虚拟资源,也包括将多个资源(比如存储设备或服务器)整合成一个虚拟资源。虚拟化技术是指实现虚拟化的具体的技术性手段和方法的集合性概念。虚拟化技术根据对象可以分成存储虚拟化、计算虚拟化、网络虚拟化等。计算虚拟化可以分为操作系统级虚拟化,应用程序级,和虚拟机管理器。虚拟机管理器分为宿主虚拟机和客户虚拟机。(Virtualization:Virtualization is a broad term that refers to the abstraction of computer resources. Virtualization hides the physical characteristics of computing resources from their users, be they applications, or end users.[15] This includes making a single physical resource (such as a server, an operating system, an application, or storage device) appear to function as multiple virtual resources; it can also include making multiple physical resources (such as storage devices or servers) appear as a single virtual resource.[15] Virtualization technology is a aggregative term of technical means and methods to implement virtualization. It can be divided to many types based on objects: storage virtualization, computing virtualization, network virtualization. Computing virtualization include:OS level virtualization, application level virtualization, hyper visor. Hypervisor include: host vm and guest vm.)
12.云计算存在的难题[1]
- 连续高可用性(Continuous high availability)
- 某个集群的失效处理
- 一致性(Consistency)
- 不同集群的同步
- 互操作性和标准化(Interoperability and standarlization)
- 在萌芽和成长期,各厂商都试图建立自己的接口API
- 所有构件的扩展(Scalability of all components)
- 信息保密(Data secrecy)
- 跨地区存储和数据传输可能会引发法律和政治问题(Legal and political problem of data store and translation across regions)
- 性能问题(Performance issue)
- 差异化定制问题(Difficulty customizing)
- 组织障碍(Organizational obstacle)
13.云计算架构[1]
云计算平台一般分为以下几层:物理设施,虚拟化,管理,服务提供。物理设施被虚拟化,提供一个灵活的资源池体提高资源利用率。管理层负责物理资源和虚拟资源池的管理、部署、监控、报警等。服务提供层组合管理层的功能提供某种形式的服务。(he physical hardware layer is virtualized to provide a flexible adaptive platform to improve resource utilization. The keys to new enterprise data center infrastructure services are the next two layers, the virtualization environment and management layer. The combination of these two layers ensure that resources in a data center are efficiently managed and can be provisioned, deployed, and configured rapidly.)
14.10个使用云计算服务的企业[1]
1. The NY Times(Amazon EC2)
2. Nasdaq(Amazon S3)
3. Major League Baseball(Joyent)
4. ESPN(Rightscale using Amazon EC2)
5. Hasbro(Amazon EC2)
6. British Telecom(3Tera)
7. Taylor Woodrow(Google Apps)
8. CSS(Amazon EC2)
9. Activision(Amazon EC2)
10. Business Objects (A SAP Company)(Rightscale using Amazon EC2)
15.云计算市场划分和参与者
云计算技术和方案提供者
3Tera - AppLogic grid OS used as cloud computing platform by service providers and enterprises
Appistry - Cloud computing middleware - Enables easily scalable cloud computing in the enterprise.
Cassatt - Cassatt Active Response platform enables administrators to set policies to power physical and virtual servers safely on and off and pool their computing resources.
CloudScale Networks - Cloud enabler. Currently in private ALPHA only
CloudHan - Cloud tech and infrastructure consultant, in China.
Enomaly Inc - Service Provider & Cloud Enabler - Developer of the Enomalism Elastic Computing Platform & Elastic Drive
Q-layer - provides software for data centers that enables cloud computing, support VSAN, VLAN, VPDC, currently support VMware ESX.
Skytap - IaaS service optimized for QA, Training, Demo, and Ops Testing. Supports VMware, Xen hypervisors & Windows, Linux & Solaris OS guests.
云计算基础设施层服务
Agathon Group - Cloud provider. Services include highly available VPS, virtual private datacenters and ready-to-use LAMP stacks. Self-service ordering. Custom development and managed services available.
Amazon Web Services - Amazon EC2/S3 (Hardware-a-a-S & Cloud Storage)
CohesiveFT - CohesiveFT Elastic Server On-Demand
ElasticHosts - UK-based instant, on-demand servers in the cloud
Flexiscale - Another instant provisioner of web servers with some advanced features like auto-scaling coming soon.
GoGrid - instant, on-demand servers offering "control in the cloud". Deploy Windows/Linux servers via web-interface in minutes
GridLayer - Cloud Provider. A service by Layered Technologies that delivers Virtual Private Datacenters and virtual private servers from grids of commodity servers
LayeredTechnologies - Cloud Provider. provider of on-demand hosting and cloud and utility computing solutions through its brand GridLayer
Mosso - Rackspace's cloud hosting service
Newservers - Instant provisioning of web servers either Windows or Linux
云计算平台层服务
Bungee Connect - Provides end to end tools and systems required to develop, deploy and host web applications (Platform as a Service)
Coherence - Oracle Coherence Data Grid for EC2 and other cloud platforms
Force.com - Salesforce.com's application development platform (PaaS)
GigaSpaces - middleware for the cloud, "cloudware"
Google AppEngine - (PaaS)Now support python
Heroku - Ruby on Rails in their Cloud
Qrimp - An AJAX based PaaS
RightScale - RightScale provides a platform and expertise that enable companies to create scalable web applications running on Amazon’s Web Services that are reliable, easy to manage, and cost less
基于云计算的服务(Saas,云存储)
CAM Solutions - SaaS Provider. Cloud Event Management, Autonomics and Monitoring-as-a-Service(TM)
CloudStatus- CloudEnabler. Real-time performance trending of cloud infrastructure (currently AWS).
Kaavo's IMOD is an easy to use online application. Cloud Computing Made Easy.
Microsoft Mesh
Nasstar - SaaS provider. Business grade Hosted Desktop service, UK market leaders.
Nirvanix - Cloud Storage
TrustSaaS - uptime monitoring and alerting service ('SaaS Weather Report') for Software as a Service (SaaS) run by an independent third party.
16.云计算开源项目[1]
Enomalism, convirt, redhat genome, hyperVM, lxlabs, LN, OpenNEbula, reservoir-fp7, scalr,eucalyptus,ganeti,gplhost,ovirt。
Useful open source projects to build cloud platform:
Kenso, hyperic, virt-P2V。
17.使用云计算服务的风险[1]
- 优先访问权风险(Privileged user access.)
- 管理权限风险(Regulatory compliance.)
- 数据处所风险(Data location.)
- 数据隔离风险(Data segregation.)
- 数据恢复风险(Recovery.)
- 调查支持风险(Investigative support.)
- 长期发展风险(Long-term viability.)
18.云计算12层模型[16]
下面是Dell描述的云计算模型:

解释:
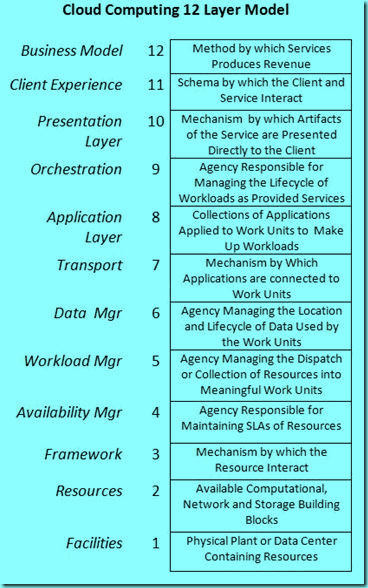
这是一个明显学术化的模型图,就像ISO七层网络模型,永远只有参考意义。
相比而言,下面这个示意图更具有表现力:
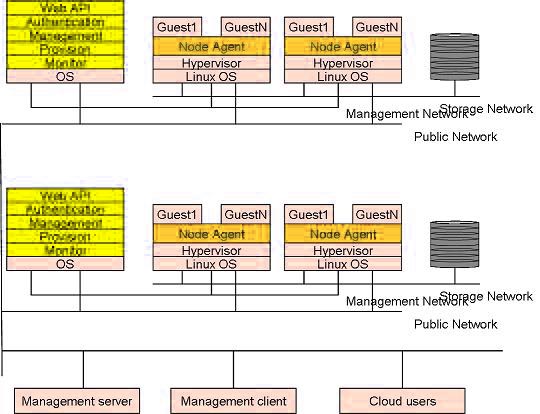
下面是DELL描述的一个数据中心
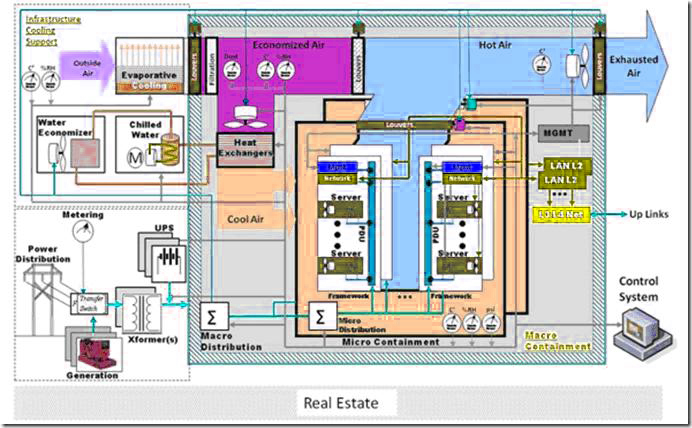
事实上,这个数据中心和传统的数据中心看起来没有很大的不同,云计算的含义是不能通过一个数据中心示意图来表达的。
19.云计算市场[17]
市场分为如下几个层次:
- Cloud Computing
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Core Cloud Services
解释如下:
- Infrastructure: the core computing resources and network fabric for the cloud deployment
- Platform: the software infrastructure that allows sys admins and developers to deploy an app to the cloud
- Core Services: additional services that can be woven into the cloud app, such as billing, storage, integration
- Applications: the ultimate cloud product - the actual cloud based application that the user touches. These number in the thousands.
市场视图
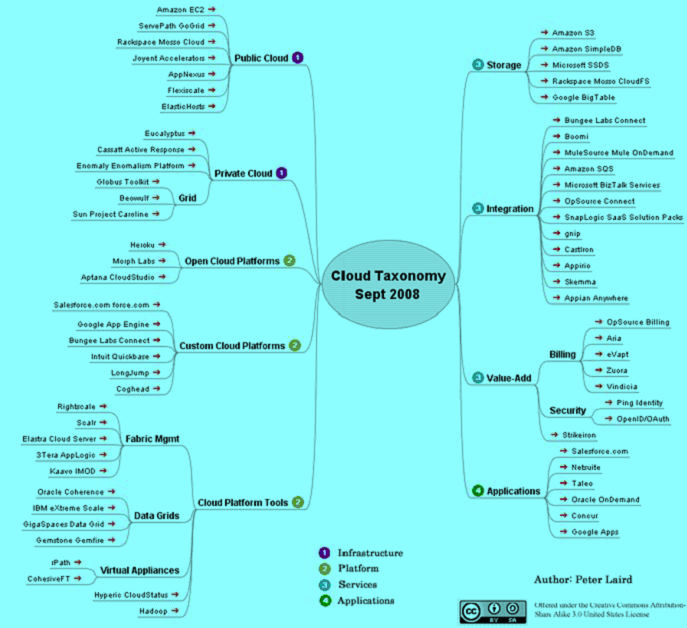
下面是市场参与者列表:
- Public Cloud
- Amazon EC2
- ServePath GoGrid
- Rackspace Mosso Cloud
- Joyent Accelerators
- AppNexus
- Flexiscale
- ElasticHosts
- Private Cloud
- Eucalyptus
- Cassatt Active Response
- Enomaly Enomalism Platform
- Grid
- Globus Toolkit
- Beowulf
- Sun Project Caroline
- Open Cloud Platforms
- Heroku
- Morph Labs
- Aptana CloudStudio
- Custom Cloud Platforms
- Salesforce.com force.com
- Google App Engine
- Bungee Labs Connect
- Intuit Quickbase
- LongJump
- Coghead
- Cloud Platform Tools
- Fabric Mgmt
- Rightscale
- Scalr
- Elastra Cloud Server
- 3Tera AppLogic
- Kaavo IMOD
- Data Grids
- Oracle Coherence
- IBM eXtreme Scale
- GigaSpaces Data Grid
- Gemstone Gemfire
- Virtual Appliances
- rPath
- CohesiveFT
- Hyperic CloudStatus
- Hadoop
- Fabric Mgmt
- Storage
- Amazon S3
- Amazon SimpleDB
- Microsoft SSDS
- Rackspace Mosso CloudFS
- Google BigTable
- Integration
- Bungee Labs Connect
- Boomi
- MuleSource Mule OnDemand
- Amazon SQS
- Microsoft BizTalk Services
- OpSource Connect
- SnapLogic SaaS Solution Packs
- gnip
- CastIron
- Appirio
- Skemma
- Appian Anywhere
- Value-Add
- Billing
- OpSource Billing
- Aria
- eVapt
- Zuora
- Vindicia
- Security
- Ping Identity
- OpenID/OAuth
- Strikeiron
- Billing
- Applications
- Salesforce.com
- Netsuite
- Taleo
- Oracle OnDemand
- Concur
- Google Apps [18]